Understand NRI Taxes with This Simple Guide
Am I a Resident Indian or a Non Resident Indian from an Income Tax perspective?
To answer this question, check your status from the following table
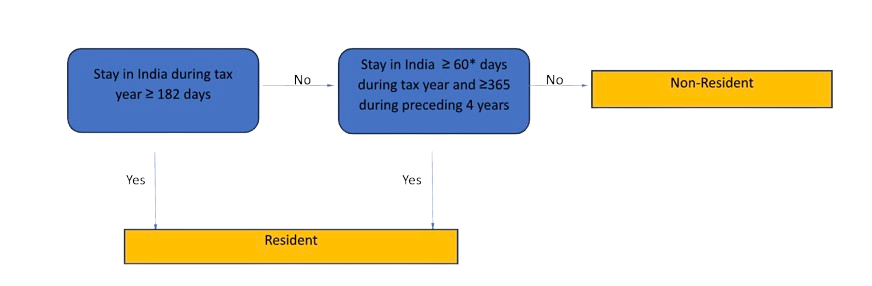
If any of the above conditions are met, person is Resident in India from Tax perspective.
If both the above conditions are not met, person is Non-Resident Indian from tax perspective.
- In respect of an Indian citizen and a person of Indian origin who visits India during the year, the period of 60 days as mentioned above shall be substituted with 182 days. The similar concession is provided to the Indian citizen who leaves India in any tax for the purpose of employment outside India.
Note: In case a of an Indian citizen or person of Indian origin whose total income, other than Income from Foreign Sources, exceeds ₹ 15 lakh during the tax year the period of 60 days as mentioned above shall be substituted with 120 days
Deemed Resident
In case of an Indian citizen/person of Indian origin earning Total Income in excess of ₹ 15 lakh (other than income from foreign sources) shall be deemed to be Resident in India if he / she is not liable to pay tax in any country.
Income Tax for Non-Resident Indians: Which types of income are subject to taxation and which are exempt?
Once your residential status is determined as NRI in any Financial Year and your income in India exceeds the basic threshold limits, you are liable to pay taxes.
NRIs are only taxed on income earned and accrued or received in India. Let us ascertain which of your incomes are subject to taxation as NRI.
Income taxable in India
-
Income earned and accrued in India, irrespective of it being received in or outside India. For example: Any dividend declared by an Indian company or rental income from residential property situated in India or gain arising on the sale of Indian investment is considered earned in India.
-
Income earned and accrued outside India but received in India. Any dividend declared by a foreign company or rental income from residential property situated outside India or gain arising on the sale of foreign investment is considered earned outside India. How ever if such dividends, rental income, or sale proceeds of investment deposited in an Indian bank account will be regarded as income received in India, and therefore, it would be taxable in India.
Income earned, accrued, and received outside India.
For example: Any dividend declared by a foreign company or rental income from residential property situated outside India or gain arising on the sale of foreign investment is considered earned outside India. Such dividends, rental income, or sale proceeds of investment deposited in any foreign bank account will be regarded as income earned, accrued, and received outside India. Therefore, it would not be taxable in India.
NRI income tax slab rates 2024-25
-
New Tax regime
| Income tax slabs (In Rs) | Income tax rate (%) |
|---|---|
| 0-3,00,000 | 0% |
| 3,00,001-7,00,000 | 5% |
| 7,00,001-10,00,000 | 10% |
| 10,00,001-12,00,000 | 15% |
| 12,00,001-15,00,000 | 20% |
| 15,00,001 and above | 30% |
Cess rate in new tax regime: 4% on tax amount
Surcharge rates in new tax regime
| Income slabs | Surcharge rate |
|---|---|
| 0-Rs 50,00,000 | 0 |
| Rs 50,00,001–Rs 1 crore | 10% |
| Rs 1,00,00,001–Rs 2 crore | 15% |
| Rs 2,00,00,001 and above | 25% |
-
Old Tax regime
-
Income tax slabs for individuals below 60 years of age
| Income tax slabs | Income tax rate |
|---|---|
| 0-Rs 2,50,000 | 0% |
| Rs 2,50,001-Rs 5,00,000 | 5% |
| Rs 5,00,001-Rs 10,00,000 | 20% |
| Rs 10,00,001 and above | 30% |
-
Income tax slabs for senior citizens
| Income tax slabs | Income tax rate |
|---|---|
| 0-Rs 3,00,000 | 0% |
| Rs 3,00,001-Rs 5,00,000 | 5% |
| Rs 5,00,001-Rs 10,00,000 | 20% |
| Rs 10,00,001 and above | 30% |
-
Income tax slabs for Super senior citizens(age 80 and above)
| Income tax slabs | Income tax rate |
|---|---|
| 0-Rs 5,00,000 | 0% |
| Rs 5,00,001-Rs 10,00,000 | 20% |
| Rs 10,00,001 and above | 20% |
| Rs 10,00,001 and above | 30% |
Cess rate under Old tax regime: 4% on tax
Surcharge rates in Old tax regime
| Income tax slabs | Income tax rate |
|---|---|
| 0-Rs 50,00,000 | 0 |
| Rs 50,00,001–Rs 1 crore | 10% |
| Rs 1,00,00,001–Rs 2 crore | 15% |
| Rs 2,00,00,001 -5 Crore | 25% |
| Above 5 crore | 37% |
Are you potentially overpaying taxes due to a lack of understanding of the Double Taxation Avoidance Agreement between India and your country of residence?
Double taxation avoidance agreement(DTAA)
DTAA is a bilateral or multilateral agreement between two or more countries to help taxpayers avoid paying double taxes on the same income. Essentially, it ensures that the same income is not taxed in two countries. India, being a significant player in the global market, has DTAA agreements with more than 90 countries, including major economies like the USA, UK, Canada, Australia, and the UAE.
Here are some key benefits of DTAA:
- Avoidance of Double Taxation: Individuals and businesses operating in multiple countries can avoid being taxed twice on the same income, ensuring they pay tax only once on income earned abroad.
- Lower Withholding Tax Rates: DTAA can provide for reduced withholding tax rates on dividends, interest, and royalties, allowing taxpayers to save on taxes.
- Tax Credits and Exemptions: Taxpayers can claim credits or exemptions for taxes paid in a foreign country, thus reducing their tax liability in their home country.
- Prevention of Tax Evasion: Helps in sharing tax-related information between countries, thereby preventing tax evasion and ensuring transparency.
- Encouragement of International Trade and Investment: By reducing the tax burden, DTAAs encourage cross- border trade and investment, fostering economic cooperation between countries.
- Dispute Resolution: Provides mechanisms for resolving tax disputes, ensuring that taxpayers are treated fairly and consistently.
How to claim benefits of DTAA
To claim DTAA benefits, individuals and businesses usually need to obtain the following:
- Tax Residency Certificate (TRC): This certificate proves that the taxpayer is a resident of a country with which the DTAA has been signed.
- Fill out Form 10F: In many jurisdictions, taxpayers must provide details about their tax residency status, as well as the DTAA agreement, through a specific form, such In India Form 10F has to be filled online on Income tax India website.
- Submit Country specific Self declaration format
Why are Form 10F and TRC important?
What is Form 10F?
Form 10F is a self-declaration form filled by NRIs/NRs receiving income from India to claim DTAA benefits. Form 10F is filled electronically and includes details like tax identification number and tax residency status.
What is a Tax Residency Certificate (TRC)?
A TRC is a document issued by the tax authorities in your resident country confirming your tax residency status, which is needed to claim DTAA benefits in India.
Consequences of not submitting Form 10F and TRC
Without Form 10F and TRC:
- Loss of DTAA Benefits: You might not qualify for reduced tax rates.
- Higher Tax Rates: Your income may be taxed at higher rates.
Filing form 10F and TRC: When and how?
When to File:
There is no strict deadline, but it is recommended to submit these forms whenever you anticipate double taxation.
How to Submit:
File Form 10F and submit the TRC via the Indian e-filing portal when filing your Indian income tax return.
What to do if your resident country doesn’t have a DTAA with India
If there is no Double Tax Avoidance Agreement (DTAA) between India and your country of residence, NRIs can still benefit from unilateral tax relief under Section 91 of the Indian Income Tax Act. This section allows NRIs to claim a tax credit for the taxes paid in both India and their home country on the same income. Essentially, it provides a way to mitigate the impact of double taxation by reducing the overall tax liability, ensuring that NRIs don’t pay tax twice on the same income.
Example:An NRI living in a country without a DTAA can claim relief under Section 91 to reduce their overall tax liability.
Conclusion
By completing the necessary paperwork and leveraging the benefits of the DTAA, NRIs can effectively lower their tax burden and prevent being taxed twice on the same income. It's essential to familiarize yourself with the specific forms you need, ensure timely submission, and maximize the tax relief options provided under Indian tax laws to safeguard your financial interests.
Author
Editorial Team of HDFC Life International
Disclaimer:
The information provided in this blog is intended for general informational purposes only. HDFC International Life and Re Company Limited, is committed to delivering accurate and up-to-date content, but we do not guarantee the completeness or accuracy of the information. The content on this blog is not meant as professional advice and should not be considered a substitute for consulting with a qualified expert in the field of insurance or financial planning and advisory matters. Decisions based on the information in this article are solely at the reader's discretion.
We may occasionally include external links to third-party websites for additional information. HDFC International Life and Re Company Limited does not endorse or have any control over the content of these external websites and is not responsible for their accuracy, reliability, or compliance with legal regulations. While we strive to offer valuable insights and guidance, the information in this blog is subject to change without notice, and we make no representations or warranties of any kind, express or implied, about the accuracy, reliability, suitability, or availability of the information provided.
By using this blog, you agree that HDFC International Life and Re Company Limited and its authors will not be held liable for any direct, indirect, or consequential damages arising from the use of the information contained here. We recommend consulting with a qualified professional for specific advice related to your unique situation.
Recommended blogs
Stay in touch
Subscribe to our newsletter and stay updated.
Related posts
HDFC International Life and Re Company Limited, IFSC Branch
FCRN: F06803 & IFSCA Registration No.: IFSCA/IIO/006/2022-23(Regulated by the IFSCA)
Registered Branch Office and Address for Correspondence: Office No. 213, Hiranandani Signature, Second Floor, Block 13B, Zone - 1, GIFT SEZ, Gift City, IFSC, Gandhinagar, Gujarat, India - 382050.
The registered marks including the name/letters "HDFC" in the name/logo of the Company/branch belongs to HDFC Bank Limited ("HDFC Bank") and the name/letters "HDFC Life" is used by HDFC Life Insurance Company Limited ("HDFC Life") and its subsidiary, HDFC International Life and Re Company Limited under a licence/agreement between HDFC Bank and HDFC Life.
For more details on risk factors, associated terms and conditions and exclusions please read sales brochure carefully before concluding a sale.
PLEASE EXERCISE CAUTION REGARDING DECEPTIVE PHONE CALLS AND FRAUDULENT OFFERS.